
We have compiled this comprehensive guide to help businesses understand their obligations related to sales tax in the state of Kansas. The guide covers various topics, including what items are subject to sales tax, how to register and file sales tax, and how to collect and remit sales tax.
In addition to providing information on how to calculate and collect sales tax, the guide also covers exemptions and special situations that may affect a business’s sales tax obligations. For example, certain types of transactions, such as those involving the sale of farm equipment or prescription drugs, may be exempt from sales tax.
By understanding the sales tax laws and regulations in Kansas, you can ensure your business complies with the law and avoids potential penalties and fines.

The Kansas state tax rate on sales consists of two parts — the state sales tax rate and any applicable local sales tax rates. The current state sales tax rate in Kansas is 6.5%, and local sales tax rates may range up to 5% depending on the location of the sale.
One of the most important things to note about sales tax in Kansas is that it is a destination-based tax. This means that the tax rate is determined by the location where the item is being delivered rather than where the seller is located.
As a result, if a business sells a taxable item and delivers it to a buyer in a different location, that business must collect the appropriate sales tax rate for that location. For example, if a business in Wichita sells an item to a customer in Kansas City, the sales tax rate will be based on the rate in Kansas City, not Wichita.
There are some exemptions to the Kansas sales tax, such as sales of food purchased with food stamps, prescription drugs and sales to nonprofit organizations. Additionally, some local jurisdictions may have additional exemptions or special rules, so businesses should consult with a tax professional at Polston Tax to ensure compliance with all applicable sales tax laws and regulations.
In Kansas, use tax is a tax on the use, storage or consumption of tangible personal property in the state that was purchased tax-free or outside the state where sales tax was not collected. Tangible personal property is an item with monetary value that has a physical presence and can be moved. Use tax ensures items used or consumed in Kansas that are not subject to sales tax elsewhere are still subject to taxation.
Businesses or individuals must pay use tax on items they bring into Kansas for use, storage or consumption if sales tax was not previously paid on those items. For example, if a Kansas resident purchases a taxable item from an out-of-state vendor and has the item shipped to Kansas, the resident would owe Kansas use tax on the item if the vendor did not collect Kansas sales tax. Any items purchased even within Kansas are also subject to use tax if the seller did not collect sales tax.
However, use tax doesn’t apply if a Kansas resident buys a product at a store in another state and transports it themselves back to Kansas, such as a souvenir bought on vacation.

The Kansas use tax rate is the same as the sales tax rate, which is currently 6.5% at the state level, plus any applicable local sales tax rates. The use tax is typically reported and paid on the Kansas sales and use tax return.
Businesses and individuals are responsible for self-reporting and paying use tax if they owe it, and failure to do so can result in penalties and interest. The Kansas Department of Revenue provides guidance on how to determine if use tax is owed and how to report and pay the tax.
In Kansas, any seller who engages in the sale of taxable services or the retail sale of tangible personal property or digital goods and services within the state must collect and remit sales tax. This includes all businesses with a physical presence in Kansas and remote sellers who meet the economic nexus threshold of $100,000 or more in sales in the state within the current or previous calendar year.
Sellers who make sales through online marketplaces or other third-party platforms are not required to collect and remit sales tax on sales made to buyers in Kansas if they don’t meet the $100,000 threshold. If sellers don’t collect tax, they should inform their customers that they must pay it directly.
Some sales may be exempt from Kansas sales tax, such as sales of food and prescription drugs. Sellers should consult a tax professional at Polston Tax to determine which items are subject to sales tax and which are exempt.

Any seller who engages in taxable sales in Kansas is responsible for collecting and remitting the appropriate sales and use tax to the state, regardless of whether the sale is made in person, online or through a third-party platform.

When it comes to Kansas sales tax, nexus plays a critical role. In Kansas, a business establishes nexus, or a taxable presence, in the state if it has a physical presence or meets certain sales thresholds. The physical presence could include having an office, warehouse, employees or other property in Kansas.
However, a business can also establish nexus in Kansas if its sales of tangible personal property or taxable services exceed $100,000, as noted above.
Once a business establishes nexus in Kansas, it must register for a sales tax account and collect and remit sales tax on taxable sales made within the state. The company may also be required to file other tax returns, such as income tax or withholding tax, depending on the nature of its activities in Kansas.
Businesses should understand their nexus obligations in Kansas and other states where they may have a taxable presence, as failure to comply with state tax laws can result in penalties and interest. Consult with us at Polston Tax to ensure compliance with all applicable tax laws and regulations.
Economic nexus applies to remote sellers who do not have a physical presence in Kansas. Remote sellers with a physical presence in the state, such as an office or warehouse, would establish nexus in Kansas based on their physical presence, regardless of their sales volume.

Remote sellers with more than $100,000 in sales in Kansas within the current or previous calendar year have economic nexus in the state. These remote sellers must register for a Kansas sales tax permit, collect and remit sales tax on taxable sales made to customers in Kansas, and file sales and use tax returns with the state.
Economic nexus thresholds can change over time, so businesses must stay up to date on the latest rules and regulations related to sales tax collection in Kansas and other states where they conduct business.
In Kansas, physical nexus is established by having a physical presence in the state. This could include:
Businesses should carefully consider their activities in Kansas to determine if they have a physical presence and must register for a sales tax permit. At Polston Tax, we can help you understand your obligations and ensure compliance with Kansas sales tax laws.
As noted above, remote sellers and marketplace facilitators who meet the economic nexus threshold in Kansas must collect and remit sales tax on taxable sales made to customers in the state. Sellers with a physical presence in Kansas must collect sales tax regardless of their sales volume.
In Kansas, most retail sales of tangible personal property and taxable services are subject to sales tax. These sales include the following:

Some types of sales may be exempt from Kansas sales tax, such as sales of food purchased with food stamps and prescription drugs. Some services, like health care and educational services, may also be exempt from sales tax. Reach out to us at Polston Tax to determine which items and services are subject to sales tax and which are exempt.
In Kansas, sales and use tax is due on most purchases. If you are unsure whether a particular sale is subject to sales tax in Kansas, or if you have questions about your company’s sales tax obligations, contact the professionals at Polston Tax. Here’s an overview of sales tax obligations beyond the general 6.5% rate.
In Kansas, hotel room occupancy may be subject to a transient guest tax, which is also known as a hotel tax, lodging tax or bed tax. This type of sales tax is specifically imposed on hotel room rentals and is in addition to the state and local sales tax that may apply to the rental.

The current transient guest tax rate in Kansas varies by county or city from 1% to 9%. The hotel or other lodging establishment typically collects this tax from the guest at the time of check-in or checkout. The lodging establishment is responsible for remitting the tax to the state and for filing regular tax returns with the Kansas Department of Revenue.
Hotels and other lodging establishments should properly collect and remit the correct amount of transient guest tax, as failure to do so can result in penalties and interest. Additionally, hotels and lodging establishments should keep careful records of all guest transactions and tax collections, as these records may be subject to audit by the Kansas Department of Revenue.
Alcohol sales in Kansas are subject to a specific excise tax. In addition to the excise tax, sales of alcohol in Kansas are also subject to state and local sales taxes, which vary depending on the location of the sale. The excise tax on alcohol varies depending on the type of alcohol and the alcohol content.
The excise tax rate in Kansas for liquor is 10% for drinking establishments, caterers and clubs.
Businesses that sell alcohol in Kansas are responsible for properly collecting and remitting the excise tax and sales tax and filing regular tax returns with the state. Keep careful records of all your alcohol sales and tax collections, as these records may be subject to audit by the Kansas Department of Revenue.
If you have questions about your company’s alcohol tax obligations or need assistance with tax compliance and reporting, consult us at Polston Tax.

In Kansas, the vehicle rental excise tax is 3.5% for the lease or rental of a motor vehicle for up to 28 consecutive days. If you rent or lease a motor vehicle, you must also pay local and state sales tax on top of the vehicle rental excise tax.
Vehicle lessees must properly pay the motor vehicle excise tax, as failure to do so can result in penalties and interest. Additionally, vehicle dealers and lessors should keep careful records of all transactions and tax collections, as these records may be subject to audit by the Kansas Department of Revenue.
If you are a vehicle lessee, dealer or lessor and you have questions about the vehicle rental excise tax, reach out to a tax professional at Polston Tax.
In Kansas, tobacco products are subject to excise taxes in addition to the state and local sales taxes that may apply. The excise tax rates on tobacco products vary depending on the product type and the quantity sold.

The excise tax rates in Kansas for various types of tobacco products are as follows:
Businesses that sell tobacco products in Kansas are responsible for properly collecting and remitting the excise tax and sales tax to the state and for filing regular tax returns. Keep careful records of all tobacco product sales and tax collections, as these records may be subject to audit.
In addition to the sales and excise taxes, some localities also impose some discretionary taxes. These taxes are typically used to fund specific projects or services in the community and are subject to voter approval.
Some examples of discretionary taxes in Kansas include:
Businesses and individuals in Kansas should be aware of these discretionary taxes, as they can impact the overall tax burden in the community. If you have questions about discretionary taxes in Kansas, contact us at Polston Tax.
Kansas provides several sales tax exemptions for some types of purchases. Some common examples of exemptions include:
Each exemption has specific requirements and limitations, and it’s up to the buyer to provide documentation and demonstrate eligibility for the exemption. Additionally, some exemptions may require the buyer to obtain an exemption certificate from the Kansas Department of Revenue.
If you have questions about sales tax exemptions in Kansas, Polston Tax can help.
If a business is required to collect Kansas sales tax but fails to do so, it may face penalties and interest charges for the unpaid taxes. In severe cases, the Kansas Department of Revenue may also pursue legal action to collect the unpaid taxes, including liens on the business’s assets or even criminal charges.
If a business knowingly or intentionally fails to collect and remit Kansas sales tax, it may be subject to additional penalties and fines, including:
Businesses should understand their sales tax obligations and comply with all applicable tax laws to avoid potential penalties and legal issues. If you are unsure about your sales tax obligations in Kansas or need assistance with tax compliance and reporting, discuss with a tax professional at Polston Tax.
Respond promptly if you receive a sales tax audit notice from the Kansas Department of Revenue. Here are some steps you should consider taking:

Be proactive and professional in your response to a sales tax audit notice. By being well-prepared and working with us at Polston Tax, you can help ensure a smoother and more successful audit process.
If you are subject to a sales tax audit by the Kansas Department of Revenue, you can expect the auditor to conduct a thorough review of your business records and financial information. The auditor checks that you have properly collected and remitted sales and use taxes in compliance with state laws and regulations.
Here are some things you can expect from a sales tax auditor in Kansas:
If your business is required to collect and remit sales and use taxes in Kansas, you need to register with the Kansas Department of Revenue. After you receive your permit, you can begin collecting sales tax on taxable sales made in Kansas. You must file regular sales tax returns and remit collected tax to the state according to the schedule determined by your estimated tax liability.
To register for a sales tax permit in Kansas, you can follow these steps:

Once you receive your sales tax permit, you should display it in a prominent location at your business. You may also need to provide a copy of your permit to your vendors, suppliers and other relevant parties.
Make sure to keep your permit in a safe place and stay updated on any changes in Kansas sales tax regulations that may affect your business.
To file your Kansas sales tax return, you can follow these steps:
Sales and use tax laws and regulations can change frequently. Stay informed about any changes affecting your business and update your tax compliance procedures accordingly.
The due dates for Kansas sales tax returns vary depending on your filing frequency. Here are the due dates for each filing option:
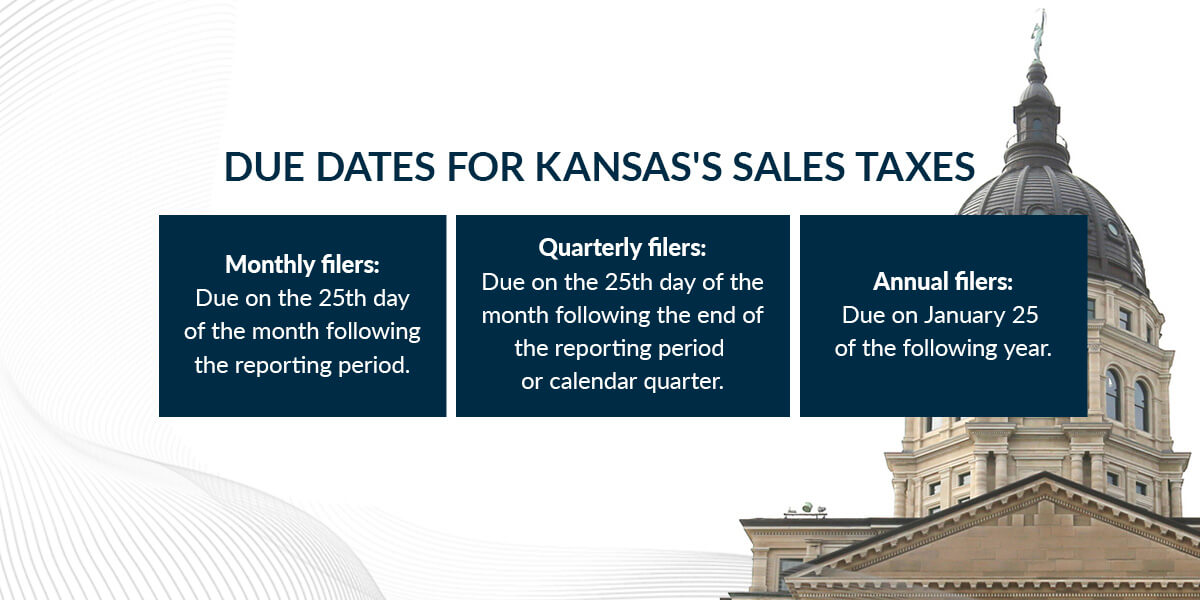
If you fail to file or pay your sales tax on time, you may be subject to penalties and interest.

To collect sales tax in Kansas, follow these steps:
By following these steps, you can ensure that you properly collect sales tax in Kansas and meet your obligations as a seller.
In Kansas, sales tax is generally applied to the total sales price, including any charges for shipping and handling. If you charge your customers for shipping and handling, you must include those charges in the total sales price used to calculate the sales tax owed.
Review the Kansas Department of Revenue’s guidelines to determine the specific rules that apply to your business and ensure you properly collect sales tax on shipping and handling.
At Polston Tax, we have a team of over 100 tax professionals, including attorneys, certified public accountants (CPAs), accountants and financial analysts. Our team includes accountants licensed in Kansas who are knowledgeable about the particular tax laws in this state. In addition to state-specific knowledge, we are licensed nationwide to provide comprehensive support.
Your business operations may leave you with little time to think about business taxes like sales tax. If you need assistance, Polston Tax can help. We provide small business tax and accounting services. If you’ve been audited for your sales tax, we can provide representation to help you through the process. Explore our services in more detail, or reach out to us online for help.